Sws101_unit3_journal
Introduction
For unit 3 journal, we have go through Try Hack Me room OWASP Top 10-2021. In this room, we are going to learn about OWASP topicthat includes details on the vulnerabilities,how they occur and how we can exploit them. We have to put theory into practical by completing supporting challenges.
The OWASP topic includes:
- Broken Access Control
- Crytographic Failures
- Injection
- Insecure Design
- Security Misconfiguration
- Valuerable and Outdated components
- Identification and Authentication Failures
- Software and Data Integrity failures
- Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
- Server-Side Request Forgery(SSRF)
Accessing Machines
We are going to access these machines by connecting with OpenVPN. To do that we have to download the vpn file and connect it through terminal.
1
sudo openvpn file-path
1. Broken Access Control
Broken Access control is a common and critical security vulnerability that arises when access control mechanisms are waek, improperly implemented or not enforced effectively. This allows unauthorized or regular users to gain access to sensitive data, system or functionalities.It also occurs when an application fails to properly enforce access controls, allowing attackers to bypass authorization and perform tasks as if they were a legitimate user.
Consequences:
- Data Breaches
- Account Takeover
- System Takeover
- Unauthorized Modification
Prevention:
- Strong authorization and authentication
- Regualr Access Reviews
- Session management
Insecure Direct Object reference
It is a specific type of Broken Access Control vulnerability. It occurs when an application uses user-supplied input to directly access object without proper authorization checks. This allows attackers to manipulates references and gain unauthorized access to resourse. Impacts of IDOR are Data Breaches and Unauthorized Actions. Data breaches is when attackers can access sensitive data of other users, leading to privacy breaches or identity theft. And unauthorized action is when attacker are able to perform actions they shouldn’t be allowed to on someone else’s account.
2. Crytographic Failures
It is a security vulnerabilities that arise when system don’t safegurad sensitive data using crytography effectively. It can also arise from the misuse of crytographic alogrithms for protecting sensitive information.
An example for crytographic failure is The Heartbleed bug(2014). It was serious flaw in OpenSSL, encryption software that powers a lot of secure communicaton on the web. The SSL standard includes a heartbeat option, which allows a computer at one end of an SSL connection to send a short message to verify that the other computer is still online and get a response back. Researchers found that it’s possible to send a cleverly formed, malicious heartbeat message that tricks the computer at the other end into divulging secret information. Specifically, a vulnerable computer can be tricked into transmitting the contents of the server’s memory, known as RAM. lots of company such as Google, Tumblr, Dropbox, Netflix, Yahoo and Facebook were affected by this bug.
Crytographic failure often end up in web apps accidentally divulging sensitive data. The data can be broadly categorized into two main areas, that is Customer Data and Technical Information. Under Customer data, it includes information that can be used to identity a specific individual and financial information. This kind of exposure can cause severe consequence for both the customer and the wen organization. Another one is exposure of technical information which i6. Valuerable and Outdated componentsncludes username and password where attacker can hijack account and steal further data, API keys and Access Tokens where attacker can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or functionalities.
In Crytographic failure(Supporting Material 2) we are introduced to new online tool called Crackstation. This tool is used craking weak password hashes.
3. Injection
Injection attacks are a common and dangerous type os cyberattack that exploit vulnerabilities in the how application handles user input. It occurs when an attacker inserts malicious code into input field on a web form, this code can then be executed by the application, potentially leading to a variety of negative consequences.
How it works
- Vulnerable Application: The web appication has a form where users can input data.
- Malicious Input: An attacker crafts a specially crafted input containing mailicious code.
- Insufficient Vaildation: The application fails to properly vaildate and sanitize the user input before using it.
- Code Execution: The mailicious code gets injected into the application’s backend and executes.
Some common example of Injection attack:
- SQL Injection
- targets database.
- Injected code can steal sensitive data, modify database, or even take control of the database server.
- Command Injection
- Targets the operating system of the server.
- Injected code can execute arbitary commands on the server, potentially giving attacker full control.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Targets the web browser.
- Injected code can steal session cookies, redirect users to malicious websites, or deface web pages.
- LDAP Injection
- Targets Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server used for authentication.
- Attackers can steal user credentials or disrupt disrupt directory services.
Impacts of Injection Attacks
Data Breaches: attcker can steal sensitive information.
Website Defacement: attackers can modify the content of a websites to display malicious content.
System Takeover: attcker can gain complete control of the underlying system.
Prevention for Injection Attacks
- Input validation and Sanitization
- Parameterized Queries: used it to seperate data from database commands, preventing SQLi attacks.
- Escape User Input
- Regular Security Updates
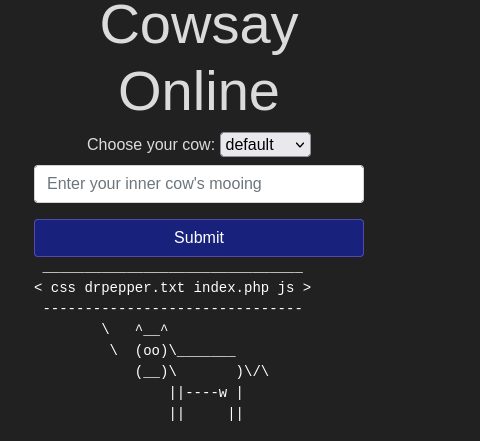
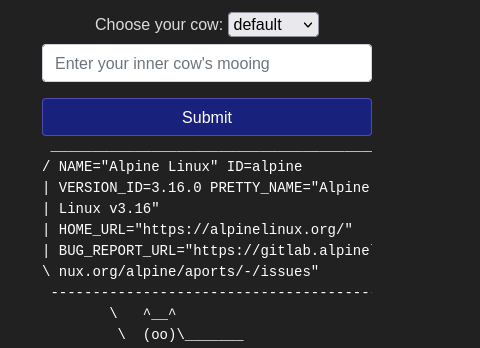
3.1 Command Injection
Command Injection occurs when server-side code in a web application makes a call to a function that interacts with the server’s console directly.
In this machine, we will complete cowsay challenge using linux commands. Common Basic commands are:
- whoami
- id
- ifconfig/ip addr
- uname -a
- ps -ef
But in this machine we will use
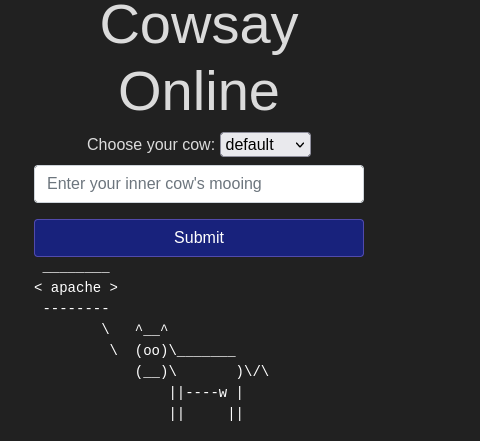
- $(ls)
- $(ls -la)
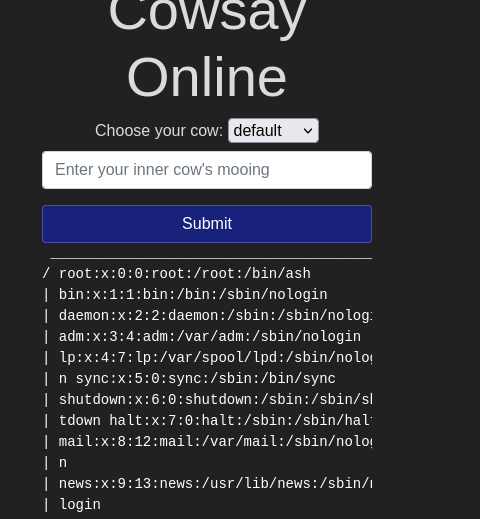
- $(cat /etc/passwd)
- $(cat /etc/os-release)
Answers for the Questions
Question 1
Question 2
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
4. Insecure Design
Insecure design, it is a fundamental flaws in the architecture and security controls of an application. It is not a specific vulnerability but it is a root cause that makes many other security weakness posiible. It happens when security isn’t considered throughout the entire development lifecycle, when application are built without proper security consideration, leaving them inherently vulnerable to various attacks.
Insecure Design happens due to lack of security expertise in the development team, rushing the development process and neglecting security best practices. It also happens when failing to properly assess the security and risk associated with the application.
Consequences of Insecure Design
Insecure design can cause security vulnerabilities sush as:
- Broken Access Control: it allows unauthorized users to access sensitive data
- Injection flaws: applicatoion might be susceptible to SQL injection and other injection attacks due to improper input validation.
- Crytographic Failure: improper use of crytographic can expose sensitive data.
These vulnerabilities can lead to serious consequences such as:
- Data Breaches
- System Takeover: attackers can gain complete control of the system.
- reputational Damage: Security breaches can damages an organization’s reputation and lead to loss of customer trust.
Prevention
- Security-focused Development: Integrate security considerrations throughout the entire development lifecycle.
- Security Testing: perform regualr security test throughout development.
- Threat Modeling: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities early on in the design phase.
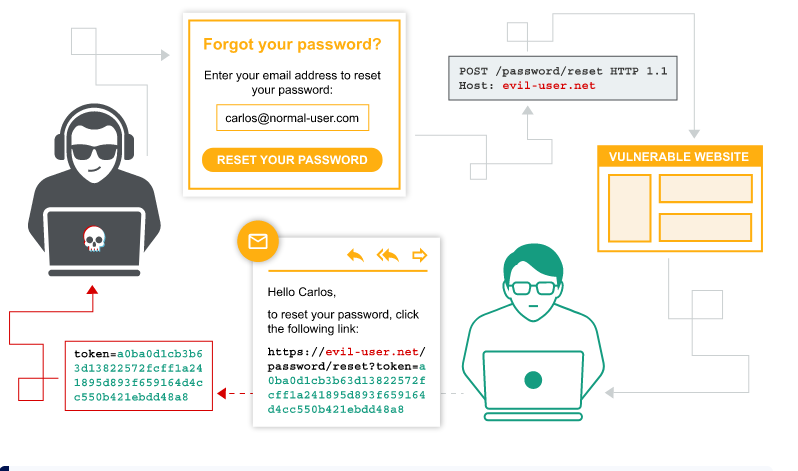
Insecure Password Resets
It can be major headache for both users and organizations. It creates an easy entry point for attackers to potentially steal account or lock out legitimate users.
Example 1
Guessable Security Questions and Unencrypted Email:
In a social media platform that allows password resets based on predefined security questions like “What’s your mother’s maiden name?” or “What’s your favorite childhood pet?”. These questions are often an easy way to guess for attackers who might have some social engineering skills or access to a user’s basic personal information. Additionally, if the platform sends the password reset link or temporary password through an unencrypted email, an attacker who has compromised the user’s email account (through phishing or malware) could intercept the email and gain access to the reset link or temporary password, ultimately taking over the social media account.
5. Security Misconfiguration
It refers to security settings or controls within a system or application that are not set correctly or left insecure. These misconfigurations can create vulnerabilties that attackers can exploit to gain unathorized access to data, system, or functionalities. Security misconfigurations can occur due to human error, where mistakes during configuration or lack of proper understanding of security settings. It also occur due to outdated configurations, when developer fails to update security settings and configurations with the latest security patches and best practices.Even when downloaded the lastest up-to-date software, poor configurations could make installation vulnerable. And when deafult accounts with unchanged passwords also lead misconfigurations.
Impacts of Security Misconfigurations:
- Increase Attack Surface: it expose vulnerabilities that attcakers can leveragee to lunch various attacks like unauthorized access, data braches and malware injection.
- Data Exposure: Sensitive data stored on misconfigured system or database might be exposed to unauthorized users.
Prventions:
- Secure Configuration Management:implemet a systematic approach to managing security configuration across systems and applications.
- Regualr Reviews and Audits: Conduct periodic security reviews and audits to identify and address misconfiguration.
- Automation: Automate security configuration management processes whenever possible to reduce human error.
Debugging Interfaces
Debugging Interfaces are tools that developers use to identify and fix bugs within their code. This provides a way to inspect the state of a program during execution, allowing developers to step through code line bu line, examine variable values, and identify where things go wrong.
Types of Debugging Interfaces:
- Command-Line Debuggers
- Traditional debugger tha operate through text-based commands.
- they offers a powerful and flexiable way to debug code.
- Examples: GDB and LLDB
- Graphical Debuggers (GUI Debuggers)
- user-friendly interfaces with graphical elements that allows developer to visualize debugging process.
- examples: Visual Studio Debugger, Eclipse debugger
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Debuggers
- have in-build debuggers that seamlessly integrate with the development workflow.
- allows developers to debug code directly within their IDE, enchancing efficiency.
6. Valuerable and Outdated components
They are the major security risk for web applications and software systems. They are essentially building blocks with known weaknesses that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to data, systems or functionalities. The main cause for Vulnerable and Outdated Components is vulnerables components and outdated components. Vulnerable Components are software components like libraries, frameworks, plugins or operating systems that conatin security vulnerabilities. These vulnerablilities can be coding error, design flaws or weaknessess in crytographic algorithms. And outdated Components are that no longer actively supported by the vendor which means they don’t receive security updates or patches, leaving them exposed to known vulnerabilities that have already been fixed in newer versions.
Why they are risky
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: attackers can exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated components to launch various attacks.
- Lack of Vendor Support: often lacks security support from vendor, users are left on their own to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Increases attack surface
Prevention
- Software Inventory and Update Management: regular check for updates and patch vulnerabilities promptly.
- Stay Informed: keep updates on the latest security vulnerabilities affacting commonly used components.
- Securtiy Scanning: utilize security scanning tools to identify vulnerabilities in your componenments and prioritize patching critical ones.
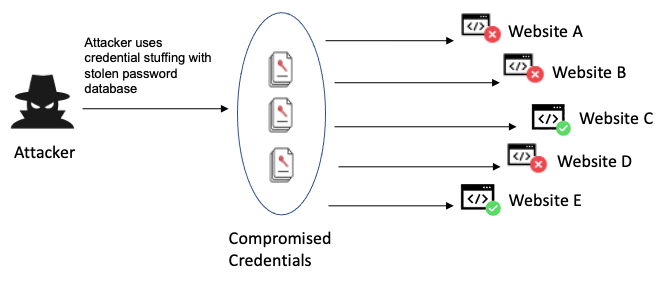
7. Identification and Authentication Failures
Identification and Authentication Failures are security weakness that occur when a system or application fails to correctly identify or authenticate a user. This lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, systems by malicious attackers. It is a critical vulvernabilities highlighted in the OWASP Top web application security risks. Identification and Authentication Failures arise due to weak or reused password, lack of Multi-factor authentication, brute-force attcks and broken authenticatin mechanism. Weak or resued password often makes easier for attackers to crack passwords or use them in credential stuffing attacks and when application does not add extra layer of security by requiring an additional verification factor, attacker can easily hack account due to lack of multi-factor authentication. Attacker can use automated tools to try a larger number of password combinations until they guess the correct one. Broken authentication mechanisms occurs when mechanisms can leave vulnerabilities that attacker can exploit.
Consequences of Identification and Authentication Failures:
- Account takeover: attacker can gain access to unauthorized user account.
- Privilege Escalation: attackers can escalate user privilege and gain access to more sensitive system or data.
Prevention:
- Enforce Strong Password
- Multi-Factor Authentication: this significantly improves security by adding an extra layer of verification.
- rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting on login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: conduct security conduct audits to identify and address weaknesses in authentication mechanisms.
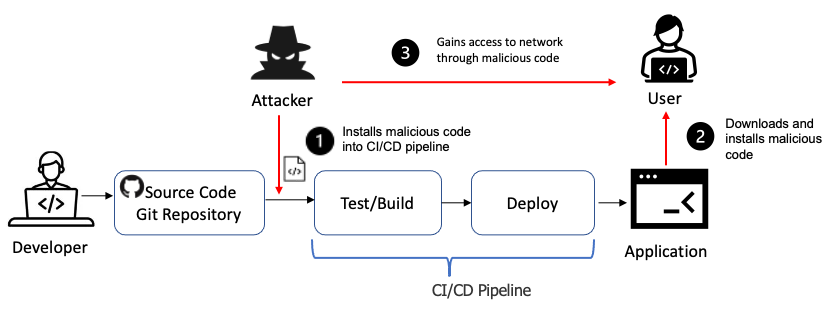
8. Software and Data Integrity failures
It arise when an application’s code or insfrastructure lacks the proper safegurads to prevent unauthorized modifications of data. This can have severe consequences as attackers can manipulate data to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information or disrupt critical systems. It occur due Insufficient data validation, missing integrity checks, and weak coding singing practices. Insufficient data validation is when a application does not have proper user-supplied data which allows attacker to inject malicious code or manipulate data to pypass security controls. Software and Data Integrity failures can occur due to unsecure data stroage, sensitive data might be stored in an unencrypted format or without proper access controls, making it vulnerable to unauthorized modification.
Consequences:
- Data breaches
- system takeover
- Disrupted operations: manipulated data can lead to disruptions in critical business processes or application.
- loss of trust: can damage an organization’s reputation and lead to loss of customer trust
Prevention:
- Data validation: Implement robust data validation practices to ensure data inttegrity and prvent malicious code injection.
- Secure data storage: encrypt sensitive data and provide proper accesss control.
- Regular security testing: condcut regualr security testing to identify and address vulnerabilities in software and data integrity controls.
- Strong code signing: Implement this to verify the authencity and integrity of software updates.
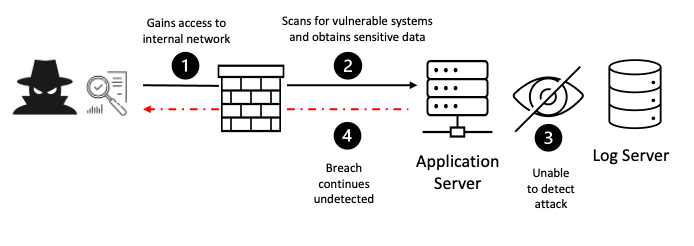
9. Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
This describes the scenario where an organization neglects to properly record(logs) and oversee security incidents within their system and application. This lack of visibility makes it difficult to detect suspicious activity, investigate security incidents and take timely action to mitigate threats. Causes of Security Logging and Monitoring Failures is insufficient logging, lack of log monitoring and unsecure ligs. When security logs are not adequately protected from unauthorized access this could allow attackers to delete or modify logs to cover their tracks. Even if the logs are generated, developers might not monitore it on a regular basis so this allows attackers to operate undetected for extented periods.
Consequences
- Delayed Dectection of Attacks: without a proper logging and monitoring, security incidents might go unnoticed for a long time, allowing attackers to do further damages.
- Limited forensic Ananlysis: security logs are crucial for forensic analysis after a security incidents. Without them, it is difficult to indentify the root cause of the issues and prevent similar attacks in the future.
Prevention
- Implement Centralized Logging: collect logs from all relevant systems and application into a central repository for easier monitoring and analysis.
- Secure logs: store logs securely and provide access to authorized personnel only.
- Regualar Log Review: dedicate rescources to review logs on a regular basis and investage any potential security incidents proptly.
- Focus on Log Content: Ensure logs capture detailed information about events, including timestamps, usernames, IP addresses, actions performed, and any relevant data involved.
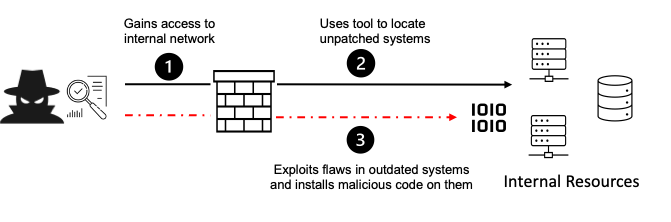
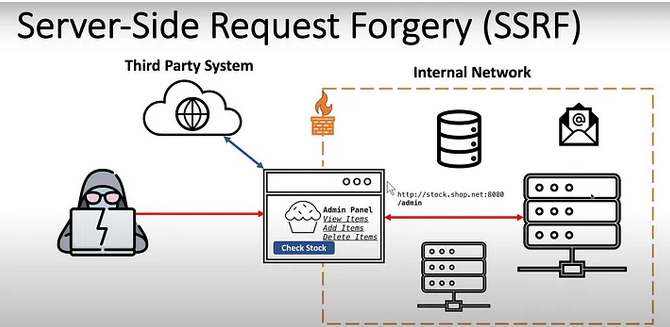
10. Server-Side Request Forgery(SSRF)
SSRF is web security vulnerability that attackers can exploit to trick a web server into making unauthorized requests to an external server. An SSRF vulnerability is like a malicious party forging a request in your name, instructing the assistant to perform unauthorized actions. SSRF occurs due to malicious input and exploiting the vulnerability.
Consequences:
- Internal network Attacks: attackers can exploit SSRF to pivot their attacks within the organization’s internal network, targeting resources that wouldn’t be accessible from the internet.
- Data Breaches
- System Takeover
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers can use SSRF to launch DoS attacks by causing the server to overload itself by making excessive requests to external resources.
Prevention:
- Input validation
- keep Software Updated
- Restrict Allowed URLs: Whitelist only authorized URLs that the application should be allowed to fetch data from.
- Sandboxing untrusted Requests: If external requests are necessary, implement sandboxing mechanisms to restrict the resources and actions the fetched data can perform.
Overview all the vulnerabilities
To make it short, by understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing recommended security measures, organization can significantly improve their overall security posture and protect their systems, data and users from vast array of cyberattacks.