Dbs101_flippedclass9
Query Optimization
Materialised Views
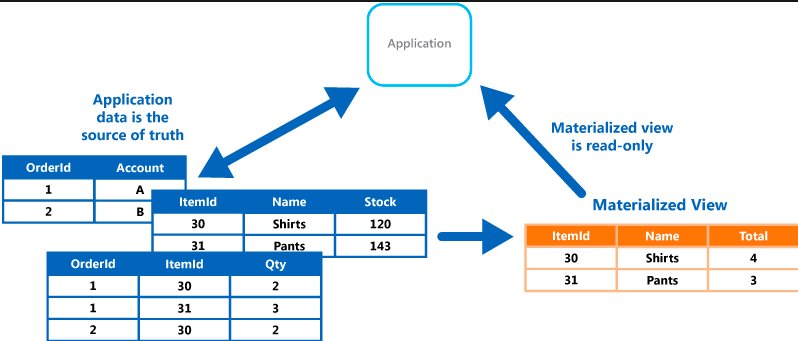
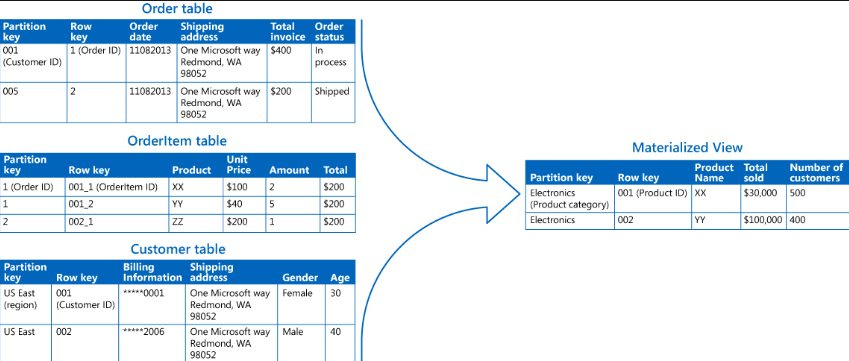
Materialized views are essentially pre-computed versions of database queries. Instead of running the query every time it’s needed, the database stores the results as a separate table, which can be queried much faster.
When a materialized view is created, the database executes the specified query and stores the results in a separate table. This table can be updated periodically or based on triggers (events in the database).
Important points
Maintenance: Materialized views need to be kept up-to-date with the underlying base tables. This can be done automatically by the database or manually by the user.
Materialized views are ideal for complex queries, frequently used queries, and data warehouses where summarizing large datasets is common.
Advanced Topics in Query Optimization
Multi-Query Optimization : When dealing with batches of queries, the optimizer can identify common subexpressions (repeated parts of queries) and evaluate them only once. This reuse reduces overall processing time.
Query Explainers : These tools provided by most databases analyze query and reveal the chosen execution plan. This plan details how the database will retrieve data, including the order of operations and indexes used. By understanding the plan, we can identify bottlenecks and optimize the query accordingly.
Parametric Query Optimization : For queries with parameters (variables), the optimizer can pre-compute optimal execution plans for different parameter values. This way, the best plan is readily available when the query is executed with specific values.
Table Partitioning : Dividing large tables into smaller, manageable partitions based on a specific column can significantly improve query performance. Partitions allow the database to focus only on relevant data, reducing processing time.
Cost-Based Optimization : The query optimizer estimates the resource consumption (cost) of different execution plans for a query. This cost analysis considers factors like I/O operations, CPU usage, and data transferred. Based on these estimates, the optimizer chooses the plan with the lowest predicted cost.
By analyzing query execution plans, identifying bottlenecks, and applying these advanced techniques, we can significantly improve the performance of our database queries.
During flipped class
During this flipped class we were divided into four groups and were asked to discuss the topics provided in the instruction. After that we are grouped into two and asked to prepare quiz questions for the other group. This session was refreshing and we learned a lot from preparing questions as well as answering questions prepared by our mates.