Dbs101_flippedclass6
Non-relational databases
It is also known as NoSQL database, are the type of database management which are designed to handle unstructured, semi-structured, or structured data in a more flexible manner.
Characteristics of non-relational database
- schema less : non- relational database do not force rigid schema.
- scalability : deals with large volumn of data and they can scale horizontally across multiple servers or nodes.
The benefits of a non-relational database
- Massive dataset organization : can store massive amount of data and also query these dataset at ease.
- Flexibility with Schema : it allows developers to store without a predefined structure.
- Scalability : horizontal scalability enables to handle large amount of data making it well suited for rapidly growing data needs.
- High performance : delivers high performance for reading and writing operations by employing techniques.
- Cost-effectiveness : are cost-effective while dealing with large-scale deployments or cloud-base environment.
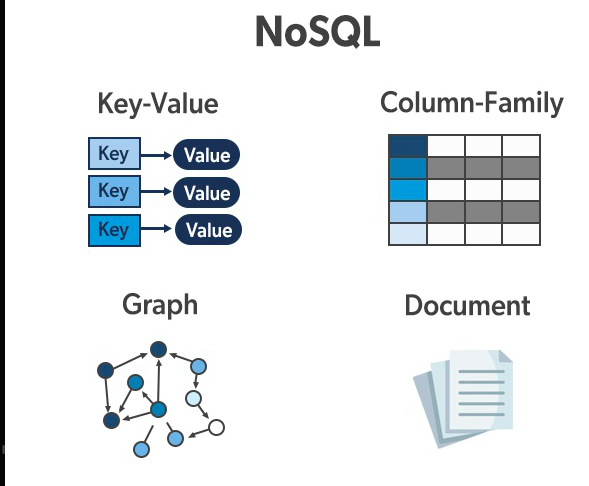
Types of Non-Relational Database
- Document-based database
- Key-Value based database
- Graph Database
- Vector Database
- Time-series Database
- Column oriented Database
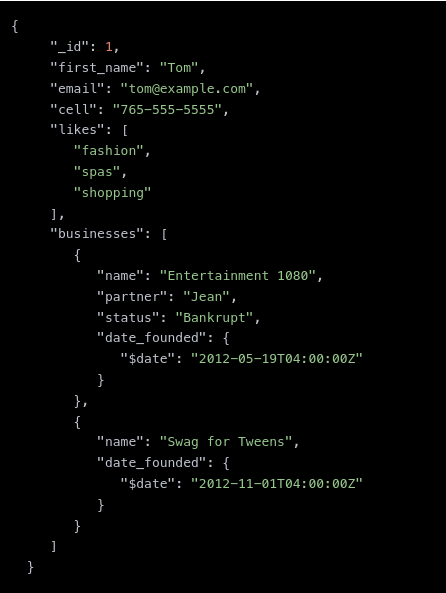
1. Document-based database
Unlike relational database, it uses the documents to store data in the database. It is more like how books are arranged in the library. A document database stores data in JSON, BSON, XML documents.
In the document darabase, the particular elements can be accessed by using the index value that is assigned for faster querying.Moreover, developer don’t have to worry about manually splitting related data across multiple tables when storing it.
Strenghts of Document-based Database
- document model is ubiquitous, intuitive and enables rapid software development.
- The flexible schema allows for the data model to change as an application’s requirements change.
- easy query language that allow developers to easily interact with their data.
- Document databases are distributed and resilient.
Weakness of Document-based Database
- do not support multi-document ACID transactions.
- data integrity challenges.
- even though it is schema-less. this flexibility can lead to challenges in mananging schema evolution over time.
Application of Document-based database
- Customer data management and personalization
- Mobile apps
- Payment processing
- Operational analytics
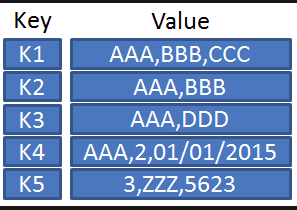
2. Key-Value based database
It is the simplest dorm of a NoSQL database. Every data element in the database is stored in key-value pairs. It is more like how dictionary are used in real life. Key features of the key-value store is simplicity, scalability and speed.
Strenghts
- They scale horizontally and automatically distribute data across servers to reduce bottlenecks at a single server.
- ease of use
- Unlike relational databases, key-value databases don’t have to perform resource-intensive table joins, which makes them much faster.
Weakness
- Key-value databases struggles to handle concurrent updates to the same key efficiently, especially in distributed environments.
- Storing large numbers of small values results in wasted storage space and increased memory usage.
- Some key-value databases offers only eventual consistency or limited transactional guarantees, which may not be sufficient for applications requiring strong consistency or complex transactional logic.
Application
- it is used in session-oriented application, such as a web application, starts a session when a user logs in to an application and is active until the user logs out or the session times out.
- it is also used in e-commerce websites which receive billions of orders per second during the holiday shopping season as it can handles the scalling of large amount of data.
- key-value database used for storing data temporarily for faster retrieval.
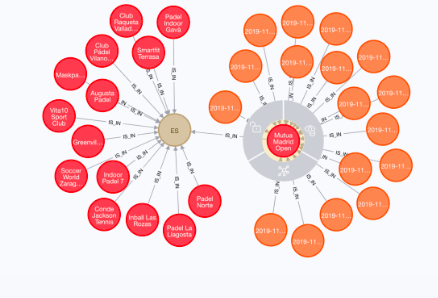
3. Graph Database
It focus on the relationship between the elements and stores data in the form of nodes in the database. Connection between the nodes are called links or relationships. The key features of graph database are it is easy to identify the relationship between the data by using liks and query’s output is real-time results.
Advantages
- has ability to handle relational data, such as relationships between people, places and things.
- Graphs are a good match for complex relationships between entities.
- graph databases can be used to model complex data in many domains.
- Every entity and their relationships in the real world can be represented as a graph.
- it also supports structured and unstructured data.
Disadvantages
- it is diffcuit to model as designing an effective graph schema requires a deep understanding of the domain and the relationships between entities.
- querying large graphs can be intensive.
- maintaining effective indexes can be complex especially for graphs with heterogeneous node and relationship types.
Application
- Graph technology is the state of the art of fraud detection.
- it is use to generate personalized recommendations for products or content based on a user’s prior interests or history with the website.
- graph database is used in chatbot system.
4. Vector Database
It is collection of data stored as mathematical representations. It makes it easier for machine learning models allowing machine to be used to power search, recommendations, and text gengeration use-cases. It is also used to search similarity in the dataset.
Advantages
- it is used in machine learning.
- they are designed to handle high-dimensional data efficiently.
- Vector databases are versatile and can be applied to a wide range of use cases, including image and video search, content-based recommendation systems, document similarity analysis, genomic sequence matching, and more
Disadvantages
- the effectiveness of similarity search degrades as the dimensionality of the vectors increases.
- Vector databases may lack support for complex query operations.
Applications
- Vector databases are used in genomics and bioinformatics applications for DNA sequence similarity search, protein structure analysis, and drug discovery.
- Vector databases are employed in image and video retrieval systems for content-based searching.
5. Time-series Database
It is database optimized for time-stamped or time series data. Time series data are simply measurements or events that are tracked, monitored, downsampled, and aggregated over time. It is built specifically for handling metrics and events or measurements that are time-stamped.
Advantages
- Time series databases are specifically optimized for handling time-stamped data, enabling efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis of large volumes of time series data points.
- it handles streaming data and real-time data ingestion efficiently.
- Time series databases typically offer flexible data retention policies, allowing users to define retention periods and expiration rules for historical data.
Disadvantages
- limited support for complex transactions.
- it exhibit complex patterns which may require sophisticated modeling technique.
- Time series databases are optimized for time series data and are not suitable for storing other types of data or performing complex relational queries.
Application
- Time series databases are commonly used for monitoring and observability applications, such as system monitoring and network monitoring.
- used in financial services for analyzing market data, stock prices, and trading volumes.
- employed in healthcare for storing patient vital signs, medical sensor data, and telemetry data from medical devices.
6. Column oriented Database
Column-oriented databases are designed to store and retrieve data by column rather than by row. It stores data vertically, optimizing for analytical queries and large-scale aggregations by organizing information into columns.
Advantages
- are optimized for analytical queries that involve aggregations, filtering, and computations on a subset of columns.
- Columns in a column-oriented database typically contain homogeneous data, allowing for better compression techniques to be applied.
- it offer schema flexibility, allowing users to add or modify columns dynamically without impacting existing data or queries.
Disadvantages
- may not be well-suited for transactional workloads that involve frequent inserts, updates, and deletes of individual rows.
- Loading data into a column-oriented database can be more complex and time-consuming compared to row-oriented databases
Application
- used in healthcare analytics for analyzing electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging data, and patient telemetry data.
- are utilized in financial services for risk management, portfolio analysis, and regulatory reporting.
- are employed in business analytics applications.
What we did during Flipped class
During this flipped class, we were assigned to groups of six with four members and had to discuss the given topics. Since the instructions and reading materials were already uploaded the day before the flipped class we all were prepared for the class. After discussing it in the expert group we had to present it the home group. Flipped class sessions have improved a lot compared to the beginning. Teaching members of home also aids teaching-learning process